Imaging & radiology tests are very important diagnostic tests in modern times. They help doctors see internal organs, bones, blood vessels, and tissues without surgery. These tests can detect infections, tumors, fractures, blockages, and many other health issues at an early stage.
1. Basic Imaging
a) X-ray (Chest, Abdomen, Bones, Joints)
X-ray is the very first technique of imaging & radiology testing. It is a type of electromagnetic radiation that can pass through the human body. In medical imaging, X-rays are a technique that creates pictures of the interior of the body, helping in the diagnosis and monitoring of a variety of conditions, e.g., pneumonia and fractured bones, etc. Different tissues in the body absorb different amounts of X-rays. Dense materials like bone absorb more X-rays and appear white on the image, while soft tissues appear in shades of gray or black.
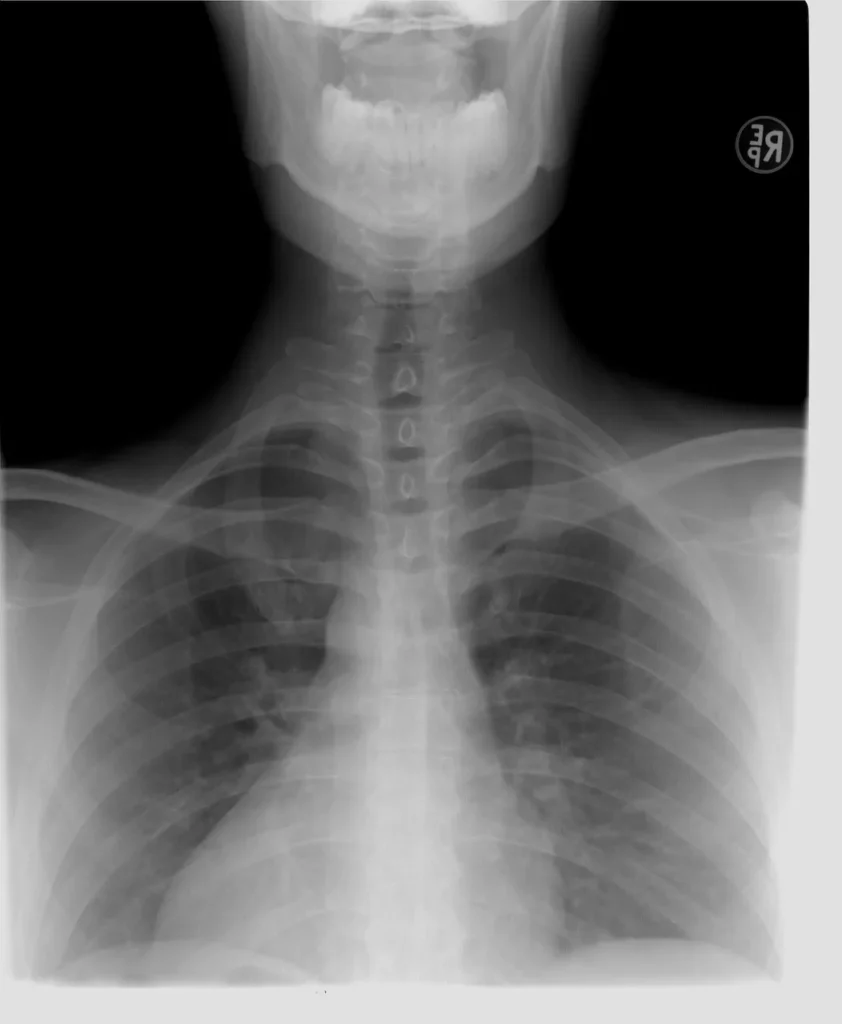
X-ray Parameters (Chest/Abdomen)
| Parameter | Normal Finding | Abnormal Finding |
| Lung Fields | Clear, no opacities | Pneumonia, TB, Tumors |
| Heart Size | Normal cardiothoracic ratio <50% | Enlarged heart (Cardiomegaly) |
| Bones | Normal alignment | Fracture, Osteoporosis |
| Diaphragm | Normal height | Free air (perforation) |
What it shows:
· Bones, lungs, heart size, abdomen gas patterns
Common Uses:
· Bone fractures, pneumonia, arthritis, intestinal obstruction
Details:
· Does it hurt? No
· Fasting required? No
· Report time: Same day – 24 hrs
· Cost: ₹300 – ₹600
b) Ultrasound (Abdomen, Pelvis, Neck, Pregnancy, Doppler)
Ultrasound, also called sonography, is an imaging & radiology test that uses high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images or videos of the inside of the body. It is a radiation-free technique commonly used in medical science.
Procedure: A handheld device called a transducer is placed on the skin after applying an ultrasound gel.
A transducer is a machine that sends sound waves inside the body. When these waves hit the tissues inside the body, they come back. The transducer captures those returning sounds. A computer converts these returned sound waves into images.
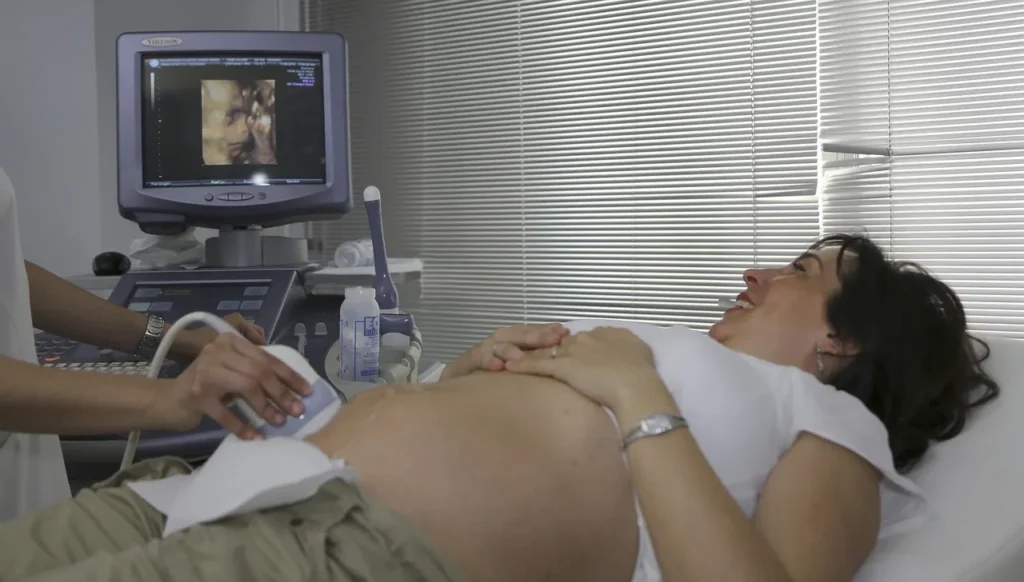
Ultrasound Parameters
| Parameter | Normal Finding | Abnormal Finding |
| Liver Size | 13–15 cm | Fatty liver, Tumors |
| Gallbladder | No stones | Gallstones, Cholecystitis |
| Kidneys | Normal size 9–12 cm | Stones, Cysts, Hydronephrosis |
| Uterus/Ovaries | Normal size & shape | Fibroids, PCOD |
What it shows:
· Liver, gallbladder, kidneys, uterus, fetus in pregnancy
· Doppler ultrasound checks blood flow
Details:
· Does it hurt? No
· Fasting required? For abdomen, yes (4–6 hrs)
· Report time: Same day – 24 hrs
· Cost: ₹500 – ₹1,500
2. Advanced Imaging
a) CT Scan (Plain/Contrast)
A CT scan is an advanced imaging & radiology test that creates real-time images of the internal organs of the body. This technique uses X-rays and a CT scan machine to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures, like bones, etc.
Procedure: The patient lies on a sliding table that goes inside a large machine. As the machine rotates around the body, it captures several X-ray images from different angles. Computer software then processes these images into detailed cross-sections.
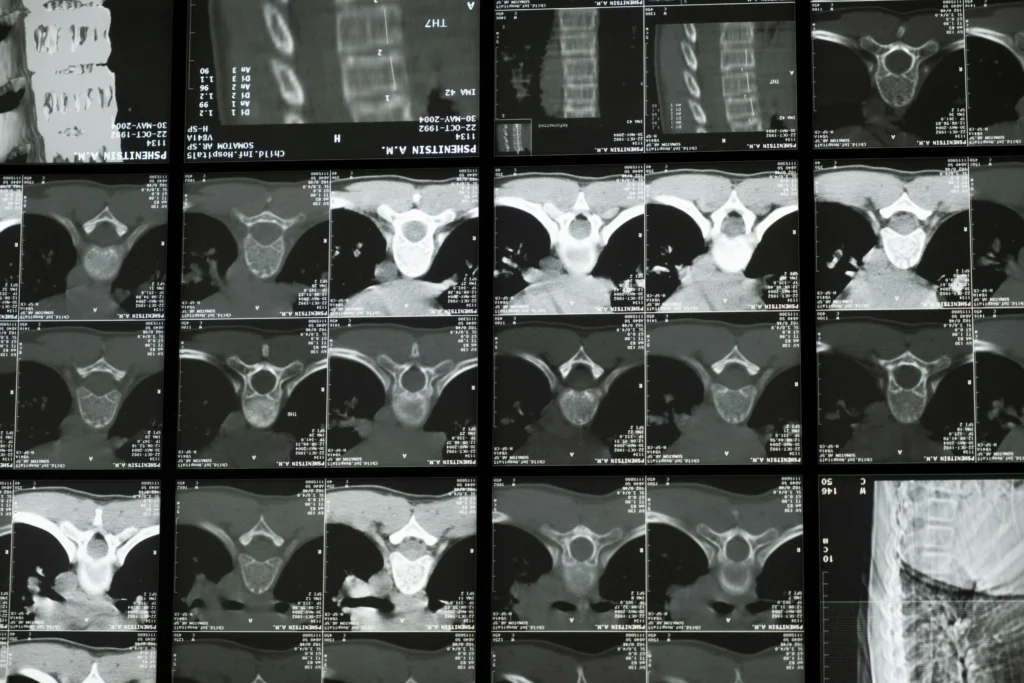
What it shows:
· Cross-sectional images of the body (3D view)
· Brain, chest, abdomen, bones
Details:
· Does it hurt? No (contrast dye may cause mild discomfort)
· Fasting required? Yes, if contrast used
· Report time: 24 hrs – 2 days
· Cost: ₹2,000 – ₹8,000
b) MRI (Brain, Spine, Joints, Abdomen)
MRI stands for Magnetic Resonance Imaging. This imaging & radiology test uses magnetic waves along with radio waves to create images of a body’s organs.
Procedure: The patient is made to lie on a table, which then goes inside a large machine. That machine then creates a very strong magnetic field and passes radio waves through the body. The waves that bounce off the body and come back are captured, and an image is created, which is called an MRI scan. It may take 15–60 minutes depending on the body part. In this process, special care is taken to ensure that no metal objects are near or no implants are placed in the patient’s body. Because when this machine creates a magnetic field, it pulls out the metal objects, and this can be fatal.
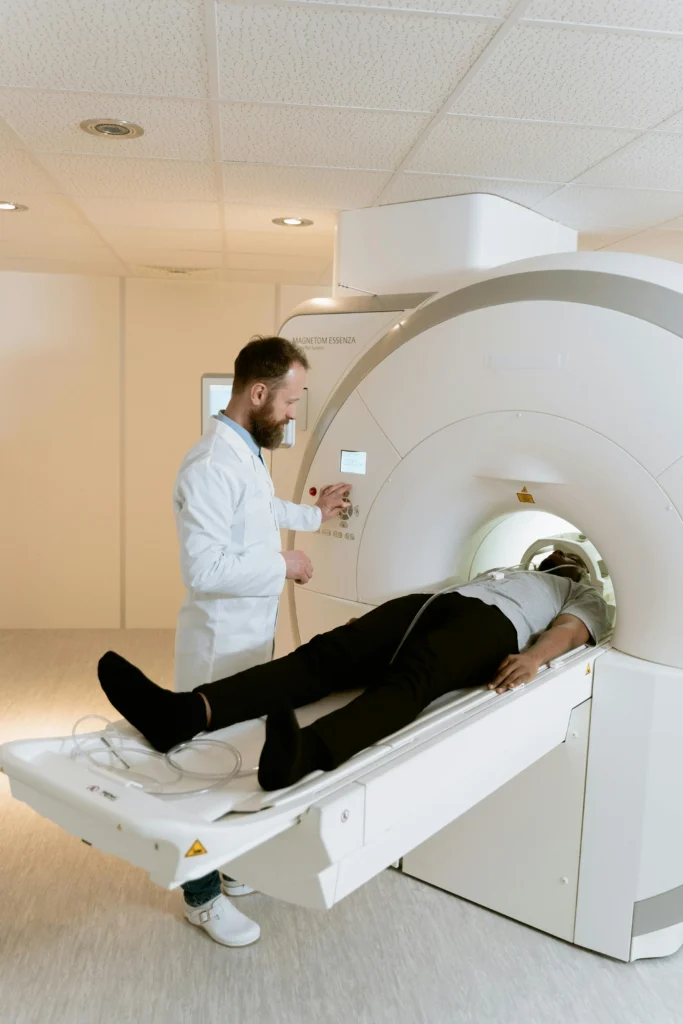
What it shows:
· Soft tissues, brain, nerves, ligaments, tumors
Details:
· Does it hurt? No (machine noise is loud)
· Fasting required? No
· Report time: 24–48 hrs
· Cost: ₹3,000 – ₹10,000
c) PET Scan
PET Scan stands for Positron Emission Tomography Scan. This is a modern imaging & radiology test technique through which the doctor can see the body parts as well as their real-time activity.
Procedure: A radioactive tracer is modified with glucose because cancer cells attract glucose. A radioactive tracer is combined with glucose and injected into the body. Since cancer cells absorb more glucose than normal cells, they absorb more of the tracer. This radioactive tracer accumulates in cancer cells and releases gamma rays, which are detected by the PET scan machine. And the PET scan machine creates an image in which we get to know the location of the cancer cells. As the radioactive tracer moves, we can see its exact movement, which helps us determine the function of the organ.
What it shows:
· Detects cancer spread, organ function
Details:
· Does it hurt? No
· Fasting required? Yes (4–6 hrs)
· Report time: 2–3 days
·Cost: ₹20,000 – ₹30,000
d) Mammography (Breast)
Mammography is a special imaging & radiology test technique developed to examine breast tissue. It is mainly used for the early detection of breast cancer.
What it shows:
· Early signs of breast cancer
Details:
· Does it hurt? Mild discomfort
· Fasting required? No
· Report time: Same day – 24 hrs
·Cost: ₹800 – ₹2,000
e) Bone Densitometry (DEXA)
Bone densitometry, also known as a DEXA scan (dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry), is an imaging & radiology testused to measure the density and strength of your bones. It is mainly used to diagnose osteoporosis and assess the risk of bone fractures. After the age of 45, women are at a higher risk of developing osteoporosis.
Bone Densitometry (DEXA) Parameters
| Parameter | Normal Range | Osteoporosis Range |
| T-score | > -1.0 | ≤ -2.5 |
| Z-score | Age-matched normal | Lower indicates risk |
What it shows:
· Bone strength and osteoporosis risk
Details:
· Does it hurt? No
· Fasting required? No
· Report time: Same day
Cost: ₹1,000 – ₹2,500
3. Cardiac Imaging
a) Echocardiography
Echocardiography, often called an echo test. A non-invasive imaging & radiology test technique that uses ultrasound waves to create detailed images of the heart’s structure and function. It helps doctors assess the heart’s chambers, valves, pumping capacity, and blood flow.
Echocardiography Parameters
| Parameter | Normal Range | Clinical Use |
| Ejection Fraction (EF) | 55–70% | Heart pumping strength |
| Valve Function | No regurgitation | Valve diseases (Mitral/Aortic) |
| Wall Motion | Normal | Heart attack damage |
· Purpose: Checks heart valves, pumping efficiency
Cost: ₹1,500 – ₹3,000
b) ECG (Electrocardiogram)
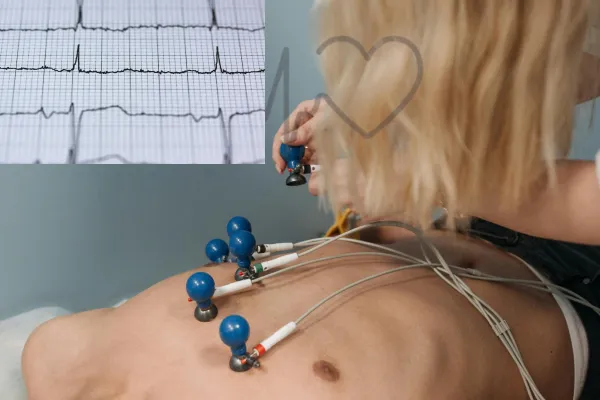
ECG stands for electrocardiogram. This is an imaging & radiology test technique that records the electrical activity of the heart. It helps doctors check the heart’s rhythm and identify any abnormalities in how the heart is working.
· Purpose: Measures heart rhythm and electrical activity
· Cost: ₹300 – ₹600
c) Treadmill Stress Test (TMT)
A treadmill stress test is also known as an exercise stress test. It is an imaging & radiology test technique in which you are made to walk on a treadmill at different speeds, and your heart rate, BP, and ECG are measured. This gives the doctor an idea about how your body reacts to stress and physical activity.
· Purpose: Monitors heart under exercise stress
· Cost: ₹2,000 – ₹3,500
4. Special Imaging
a) Barium Studies (Meal, Enema)
Barium studies are imaging & radiology tests that use barium-based contrast material and X-rays to examine the structure and function of the digestive tract.
· Purpose: Digestive tract abnormalities
· Fasting: Required (8 hrs)
· Cost: ₹1,500 – ₹3,000
b) IVP (Intravenous Pyelogram—Kidney Imaging)
IVP, or intravenous pyelogram, is a specialized imaging test used to examine the kidneys, ureters, and bladder.
· Purpose: Kidney stones, urinary tract blockages
· Fasting: Required (4–6 hrs)
Cost: ₹2,000 – ₹4,000
c) HSG (Hysterosalpingography)
HSG, or Hysterosalpingography, is a special imaging & radiology test used to examine a woman’s uterus (womb) and fallopian tubes. It helps doctors find the cause of infertility or repeated miscarriages by checking whether the fallopian tubes are open and if the shape of the uterus is normal.
· Purpose: Checks uterus and fallopian tube blockage (infertility workup)
· Cost: ₹3,000 – ₹6,000
Key Points
· Avoid unnecessary tests.
· Pregnant patients ask a doctor before X-ray/CT.
· Costs may vary depending on the city and diagnostic center.
🥴 Looking for some more medical tests? You can also read our Medical Tests—Complete A to Z Guide (With 100+ Tests) 😉
Which imaging & radiology tests are best for cancer detection?
👉 PET scans and MRIs are highly.
Are imaging & radiology tests safe during pregnancy?
👉 Ultrasound is safe; X-rays and CT scans are avoided.
How much radiation do these imaging & radiology tests use?
👉 Small amounts are not harmful.
Can I eat before the Imaging & Radiology Tests?
👉 Yes, except CT with contrast and barium studies require fasting.
How much do imaging & radiology tests cost in India?
👉 Costs range from ₹300 (X-ray/ECG) to ₹30,000 (PET scan).
- Neonatal Disorders: Silent Killers Every Parent Must Know About - September 8, 2025
- COPD Life Expectancy by Stage: What to Expect and How to Improve Your Future. - September 5, 2025
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): 3.5 million deaths in 2021. - September 3, 2025