Table of Contents
Introduction
Just think how you would feel if you went to a doctor and the doctor told you that from today onwards you should not eat sugar and eat very little salt and gave you some medicine and told you that you have to take this medicine for the rest of your life. Something similar happens in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes mellitus is one of the most prevalent chronic diseases these days, affecting millions of people worldwide. This disease is caused by high blood sugar levels and can create serious complications if not treated.
What is Diabetes Mellitus?
In simple words, diabetes mellitus is a condition when the sugar level in our blood becomes too high due to the insulin in our body becoming less or our body not being able to use insulin properly. Insulin is a substance made by the pancreas that helps change sugar into energy. Our body uses this energy to work properly. In diabetes mellitus, the body either stops making insulin or makes very little of it. Because of this, the sugar in our blood cannot be changed into energy, and the amount of sugar in the blood keeps increasing.
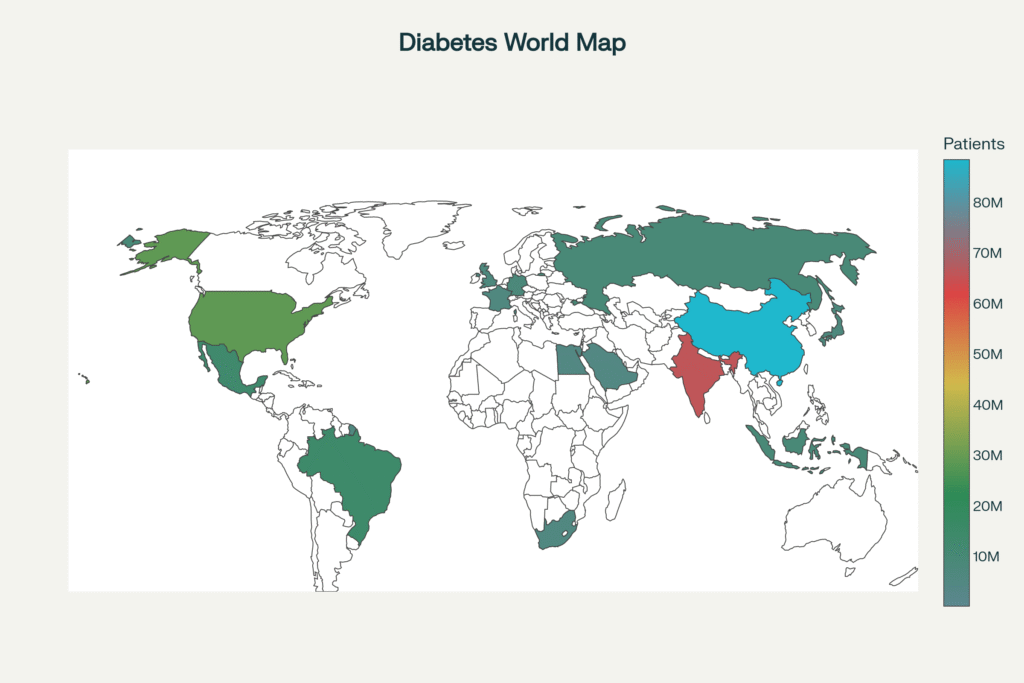
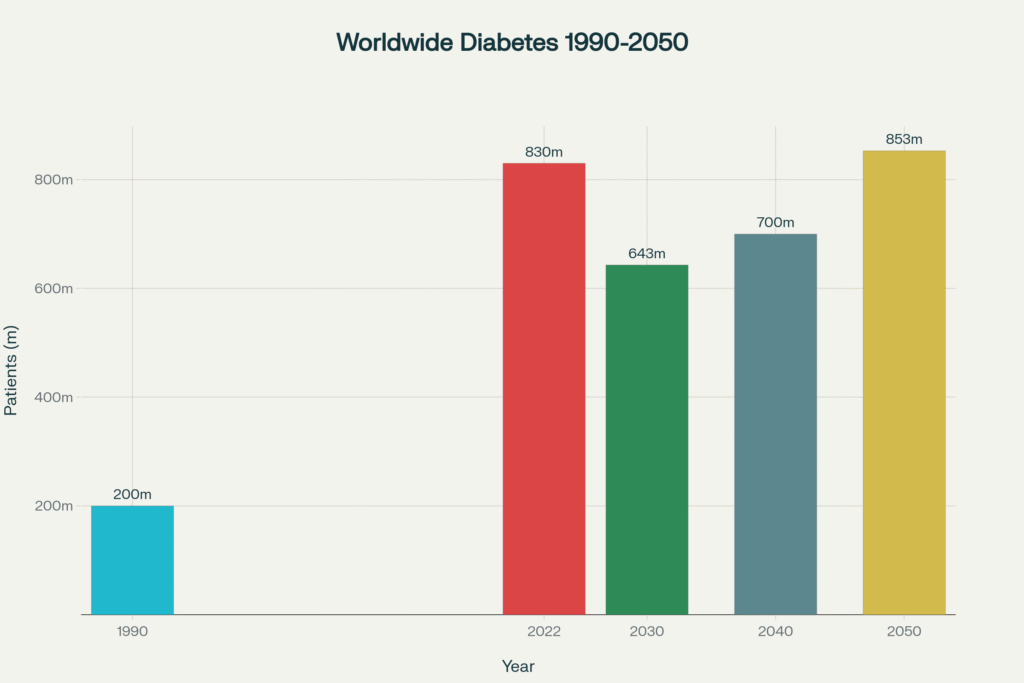
Some studies show that approximately 537 million people have diabetes mellitus worldwide.
Do you know that your high blood sugar can damage your kidneys? If you don’t, let me tell you: these days, the reality is that 1 out of every 3 people with diabetes develops kidney disease.
👉 ” click here to Discover more about Diabetic Kidney Disease“
Causes and Risk Factors of Diabetes Mellitus
Diabetes mellitus is the silent killer you must understand. Several factors can increase the risk of developing diabetes mellitus:
Non-modifiable risk Factors
🧬 Genetics: Family history plays a significant role in diabetes. If your family (father, mother, and grandparents) has a history of diabetes, there is a higher chance of having diabetes mellitus.
🎂 Age: Risk increases with age, especially after 45 years. After a certain age, insulin production decreases and other factors come into play.
🪢 Hormonal Imbalances: Certain conditions like Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) can increase the risk of diabetes mellitus.
Modifiable risk Factors
🥴 Obesity and Physical Inactivity: Extra body fat can lead to insulin resistance. Physical activity is very important to digest food and convert it into energy. If you are inactive, your body’s energy requirements decrease, and your body stores fat from food.
🍔 Poor Diet: Excess sugar and processed foods increase the risk of diabetes mellitus. There is a limited supply of insulin in our body; it can’t handle excessive sugar.

Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 – Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus:
A condition when body insulin production decreased and sometimes stopped. This happened when the body’s immune system attacked insulin-producing cells. This is also called insulin-dependent diabetes. Type 1 diabetes affects only about 5 to 10% of people with diabetes.
Type 2 – Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus:
Type 2 diabetes used to be called non-insulin-dependent. In this condition the body makes insulin but cannot utilize it properly, and sometimes the body creates resistance to insulin. It has become more common in children and teens over the past 10 to 20 years because more young people are overweight or obese. About 90% of people with diabetes have type 2.
Gestational Diabetes:
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy in women who did not have diabetes previously. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels that can affect both the mother and the baby. While it often resolves after delivery, it increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
💡💡💡 Insulin: Insulin was first discovered by Banting in 1921. It was first obtained in pure crystalline form in 1926, and the chemical structure was fully worked out in 1956 by Sanger. Insulin is a hormone produced by the β-cells of the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Symptoms and Warning Signs
· Feel hunger quickly after having food.
· Unexplained weight loss.
· Frequent urination
· Feeling thirsty soon after drinking water.
· Fatigue
· Blurred vision sometimes.
· Slow healing of sores and wounds.
👉Some symptom of Diabetes mellatus in women are difftent Click here to take a look

💡 Tip: Many people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms initially. Regular health checkups are necessary for early detection.
👉 Pre-diabetes: When your blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough for a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes. At this stage, you can control your blood glucose level by making lifestyle changes. Patient with fasting sugar between 100 and 125.
Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus
Your doctor will ask about your family medical history (if there are any diabetes cases in your family) and symptoms. The following tests are usually performed to diagnose diabetes:
Glycated Hemoglobin (HbA1C) Test
Measures the average blood glucose level for the past two to three months.
Normal: < 5.7%
Prediabetes: 5.7% – 6.4%
Diabetes: ≥ 6.7%
You can do this test at home with the help of a Hemoglobin Test Kit.
Fasting Glucose Test
Determines fasting blood sugar levels; performed in the morning before breakfast.
Normal: < 100 mg/dL
Prediabetic: 100 – 125 mg/dL
Diabetic: > 125 mg/dL
You can do this test at home with the help of a glucometer.
Click here to learn more about these tests.
Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT)
You fast overnight, and fasting blood sugar is measured. Then, after drinking a glucose-rich drink, blood sugar levels are measured after two hours.
Treatment Options for Diabetes Mellitus
Managing diabetes involves a very important factor, which is lifestyle changes, blood sugar monitoring, and medication:
Lifestyle Changes
👉 Healthy diet: Focus on high-fiber foods, whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fruits and vegetables.
👉 Regular exercise: At least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days of the week and walk at least 500 steps after every meal.
👉 Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces insulin resistance and helps control blood sugar levels.
Monitoring
Regularly check blood glucose levels to manage diabetes effectively. You can use a glucometer for testing your blood glucose level at home.
Medications
👉 Type 1 Diabetes: Insulin injections are necessary to control blood glucose levels.
👉 Type 2 Diabetes: Oral medications, non-insulin injectables, or insulin therapy may be prescribed. Metformin (Glumetza, Fortamet, etc.) is the most common medicine prescribed by the doctor for type 2 diabetes.
Prevention Tips
👉 Healthy Diet: Eat whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, and vegetables. Avoid processed foods, sweets, and sugary drinks.
💡💡💡 Click here for Best Diet Plan for Diabetes Patients
👉 Regular Exercise: At least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days, and walk 500 steps after every meal.
👉 Weight Management: If overweight, losing 7% of body weight can significantly lower the risk. You can measure your weight at home with a digital weighing scale.
👉 Medication/Insulin: Take as prescribed by your doctor.
Regular Monitoring: Keep track of blood glucose, cholesterol, and blood pressure.
Latest Research in Diabetes Mellitus (2025)
| Sr. No. | Area | Highlights | Reference |
| 1. | Cell-based therapies | Alpha‑to‑beta conversion, iPSC‑derived islet transplants, regenerative medicine | 1. Forbes (2025) 2. MedNewsPedia (2025) |
| 2. | Smart insulins | Glucose‑responsive molecules to avoid hypoglycemia | 1. Wikipedia (2024) 2. Reddit HealthTech (2025) |
| 3. | New GLP-1 pills | Orforglipron (Eli Lilly), efpeglenatide | Harald Sun (2025) |
| 4. | Ai-enabled insulin delivery | Closed‑loop systems with reinforcement learning | Forbes (2025) |
| 5. | Early detection using Ai | ECG‑DiaNet, chest‑X‑ray + EHR models | 1. arXiv ECG-DiaNet (2025) 2. arXiv Chest X-ray Ai |
| 6. | Microbiome & lifestyle | Probiotics, diet interventions, yoga prevention | 1. MedNewsPedia (2025) 2. Times of India (2025) |
| 7. | Indian biomarker research | Urinary exosome markers for early CKD detection | Times of India CKD biomarker (2025) |
| 8. | Genetic/phenotypic subtypes | Non-autoimmune type -1 variant in African‑descent populations | Reuters (2025) |
What is diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a condition when the sugar level in our blood becomes too high due to the insulin in our body becoming less or our body not being able to use insulin properly.
How many types of diabetes are there?
• Type 1: When the pancreas stops making insulin.
• Type 2: The body does not use insulin properly. Due to a heavy amount of Glucose in blood or something else.
• Gestational Diabetes: Develops during pregnancy in women without previous diabetes.
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Many people with type 2 diabetes have no symptoms initially.
• Increase in urination
• Feeling thirsty
• Fatigue
• Blurry vision
• Unexplained weight loss
What causes diabetes?
• Family history (genetics)
• Being overweight
• Poor diet
• Lack of physical activity
• Age
How is diabetes diagnosed?
• Blood sugar tests (Fasting & Post-meal)
• HbA1c test
• Glucose Tolerance Test (GTT)
Can diabetes be cured?
Unfortunately, there is no permanent cure, but it can be controlled with diet, medicines, and exercise.
What should a diabetic person eat?
• Green vegetables and low-sugar fruits
• Whole grains (wheat, oats, barley)
• Lentils, beans, dry fruits (small quantities)
• Plenty of water
What foods should be avoided in diabetes?
• Sugar and sweets
• Sugary soft drinks
• Fried and processed foods
• Too much salt
How can diabetes be controlled naturally?
• Exercise for at least 30 minutes daily
• Stay active and walk 500 steps after meals
• Reduce stress and get good sleep
• Avoid sugary foods
Are there any new medicines for diabetes?
Yes, new drugs like Orforglipron and Smart Insulin are under research.
Disclaimer
The information provided in this article is for educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a doctor for diagnosis and treatment.
- Neonatal Disorders: Silent Killers Every Parent Must Know About - September 8, 2025
- COPD Life Expectancy by Stage: What to Expect and How to Improve Your Future. - September 5, 2025
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD): 3.5 million deaths in 2021. - September 3, 2025


3 thoughts on “Diabetes Mellitus: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment & Latest Research (2025)”